
Dog Vertebral Column Anatomy ANATOMY STRUCTURE
Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The smallest known adult dog was a Yorkshire Terrier that stood only 6.3 cm (2.5 in) at the shoulder, 9.5 cm (3.7 in) in length.
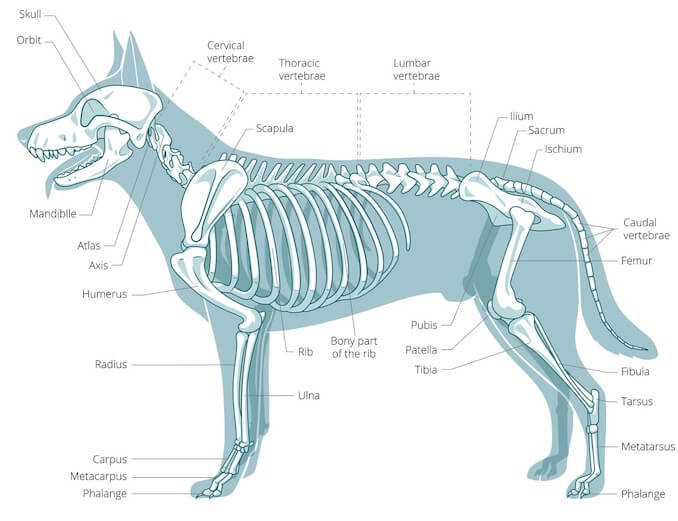
A Visual Guide to Dog Anatomy (Muscle, Organ & Skeletal Drawings) All
The skeleton is composed of the hard tissues of the body, and its primary functions are to support the body, to provide a system of levers used in locomotion, to protect the soft organs of the body, and to produce red blood cells (hematopoiesis). A dog's skeleton is formed so the dog can run fast, hunt and chase.

Dog skeleton with major bone elements labeled (Davis, 1987, p. 54
Summary Anatomy of a Dog Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Would you be surprised to know that short dogs are more aggressive? Or taller dogs are more affectionate?

Dog Anatomy Dog Skelton
The dog skeleton anatomy consists of bones, cartilages, and ligaments. You will find two different parts of the dog skeleton - axial and appendicular. Here, I will show you all the bones from the axial and appendicular skeleton with their special osteological features. Again, I will provide more labeled diagrams for each dog skeleton bone.

Anatomy Of Dog Skeleton With Labeled Inner Bone Scheme Vector
This veterinary anatomical atlas includes selected labeling structures to help student to understand and discover animal anatomy (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system). Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated.
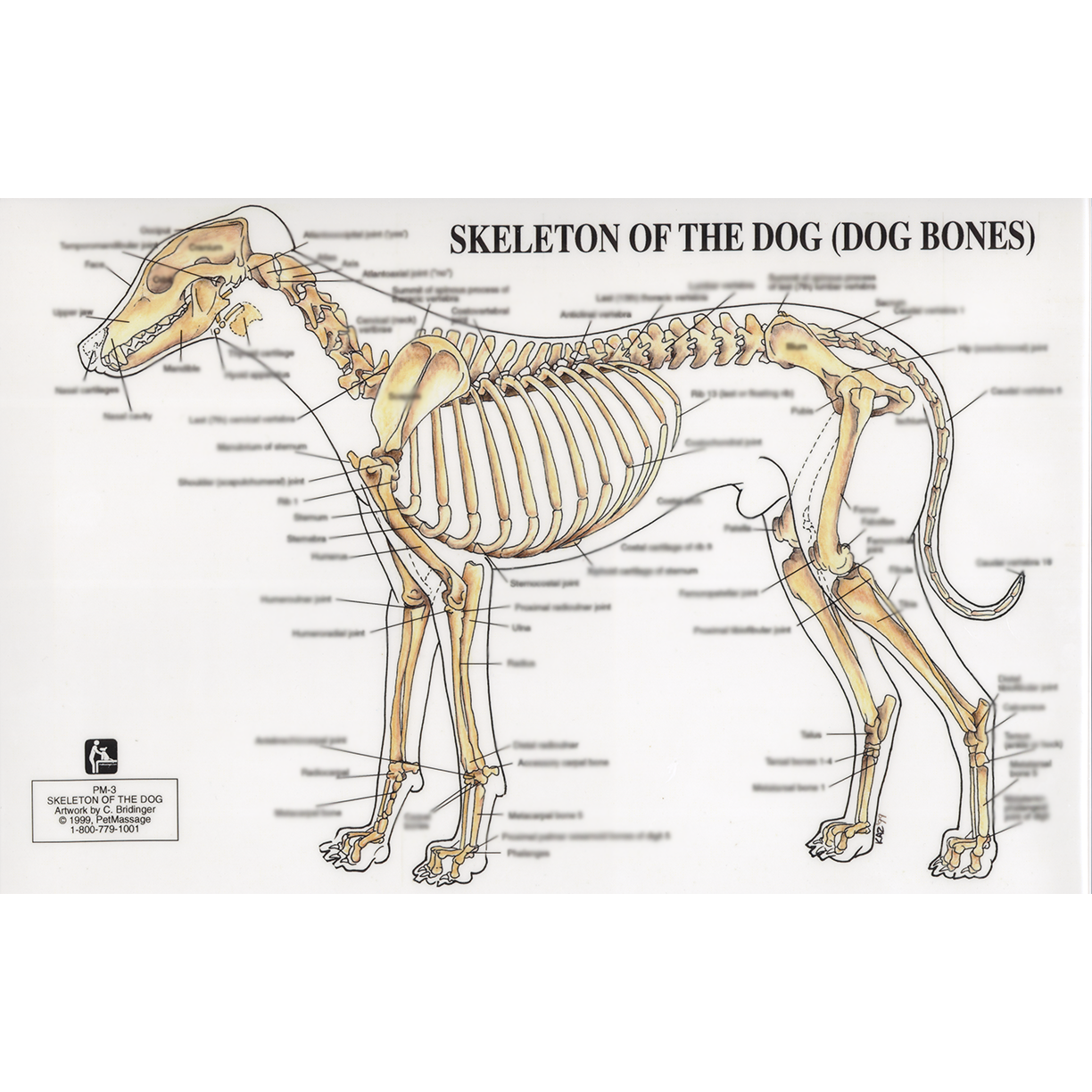
PetMassage™ Chart 3 Skeleton of the Dog · PetMassage™ Training and
Labeled anatomy of the head and skull of the dog on CT imaging (bones of cranium, brain, face, paranasal sinus, muscles of head) This module of vet-Anatomy presents an atlas of the anatomy of the head of the dog on a CT. Images are available in 3 different planes (transverse, sagittal and dorsal), with two kind of contrast (bone and soft tissues).

Vintage 1935 Dog Veterinary Print Skeleton Of Dog Anatomy Of Dog Canine
The dog skeleton is the bony part of dogs made for the support and protection of internal organs. Bones are connected through joints and muscles move the bones to produce the normal dog movements. In this article we will cover: Bone types and parts of the dog skeleton The dog skull Dog cranium The spine The Trunk The Forelimb The Hindlimb

Dog skeleton 101 Dog Anatomy Bones Animal Hackers
The anatomy of a dog includes its skeletal structure, reproductive system, the internal organs, and its external appearance. The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief, along with diagrams, which will help you understand them better. External Anatomy Dogs, like all mammals, have eyes, a nose, a forehead, and ears.
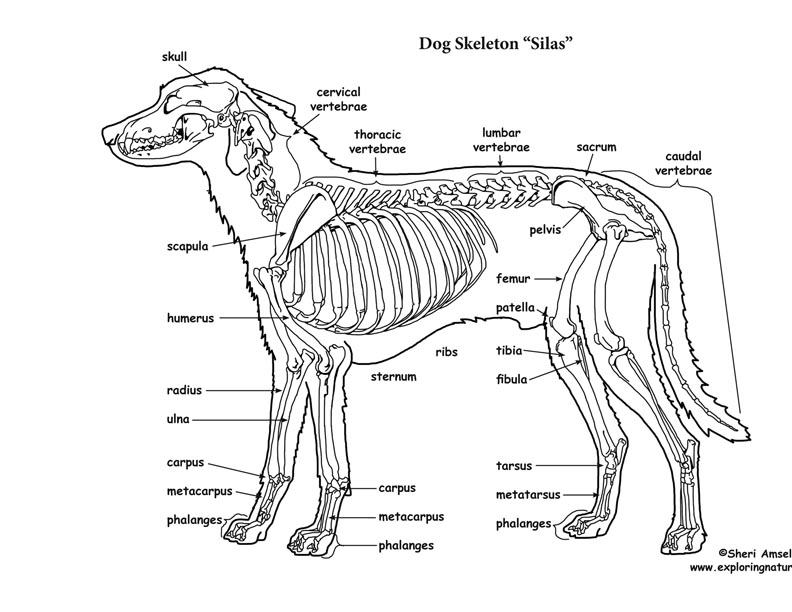
Dog Skeletal Anatomy
The Anatomage Dog is the first highly detailed dog anatomy atlas that comprehensively features internal organs, including vascular systems and muscular-skeletal structures. Originating from real dog data, the Anatomage Dog exhibits the highest level of anatomical accuracy. All of its volumetric 3D and individual structures are segmented, users.
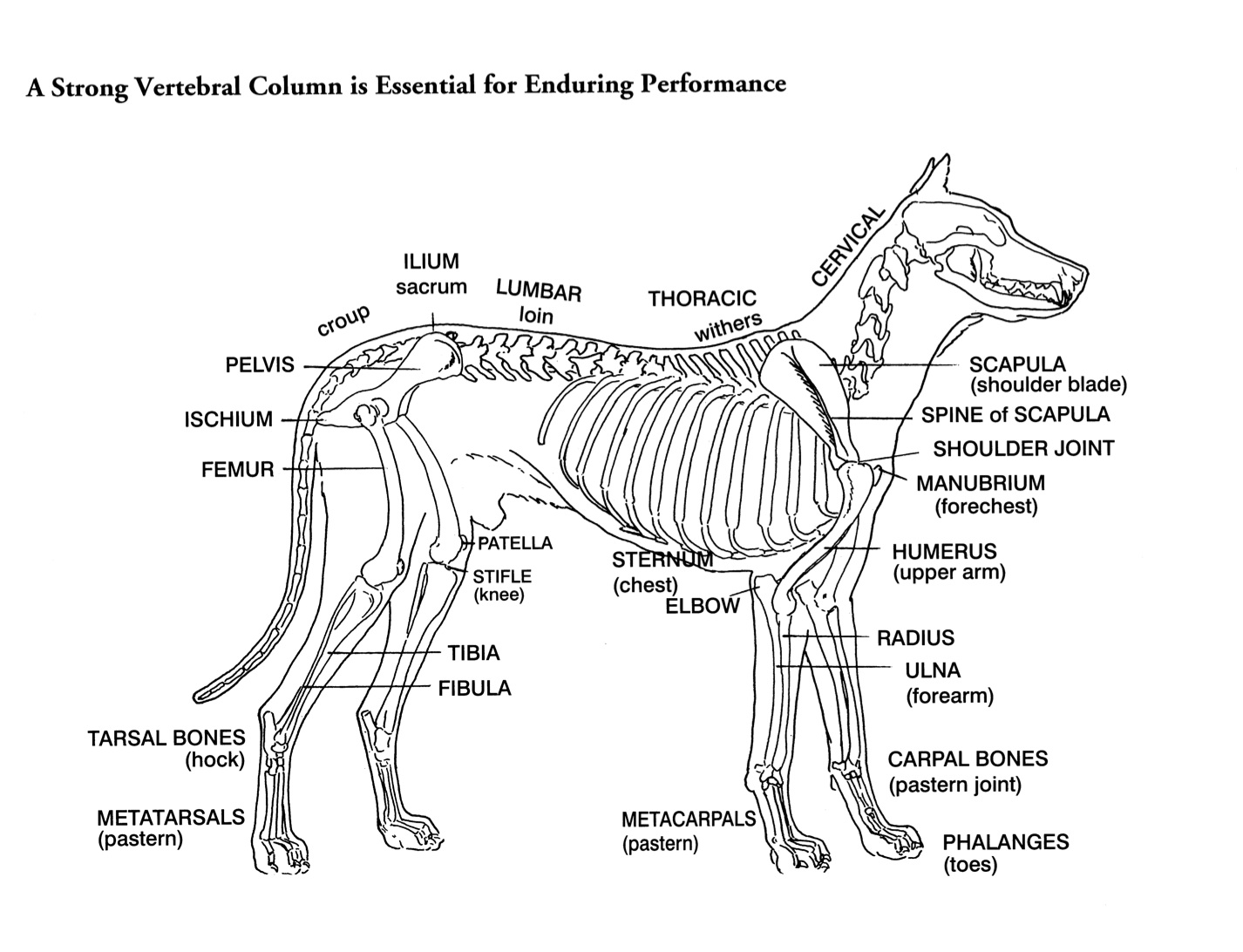
Helen King on Structure Evaluation Susan Garrett's Dog Training Blog
Dog skeleton, TBjornstad, 2006 The information below will highlight the bone anatomy of the domestic dog which will include the major and selected important minor aspects of anatomy. Very detailed anatomy of individual bones is not covered below due to space restrictions.

Dog Skeleton Anatomy
This is an overview of the canine skeleton, pointing out features that help in identification and orientation.If you find this helpful, please let me know by.
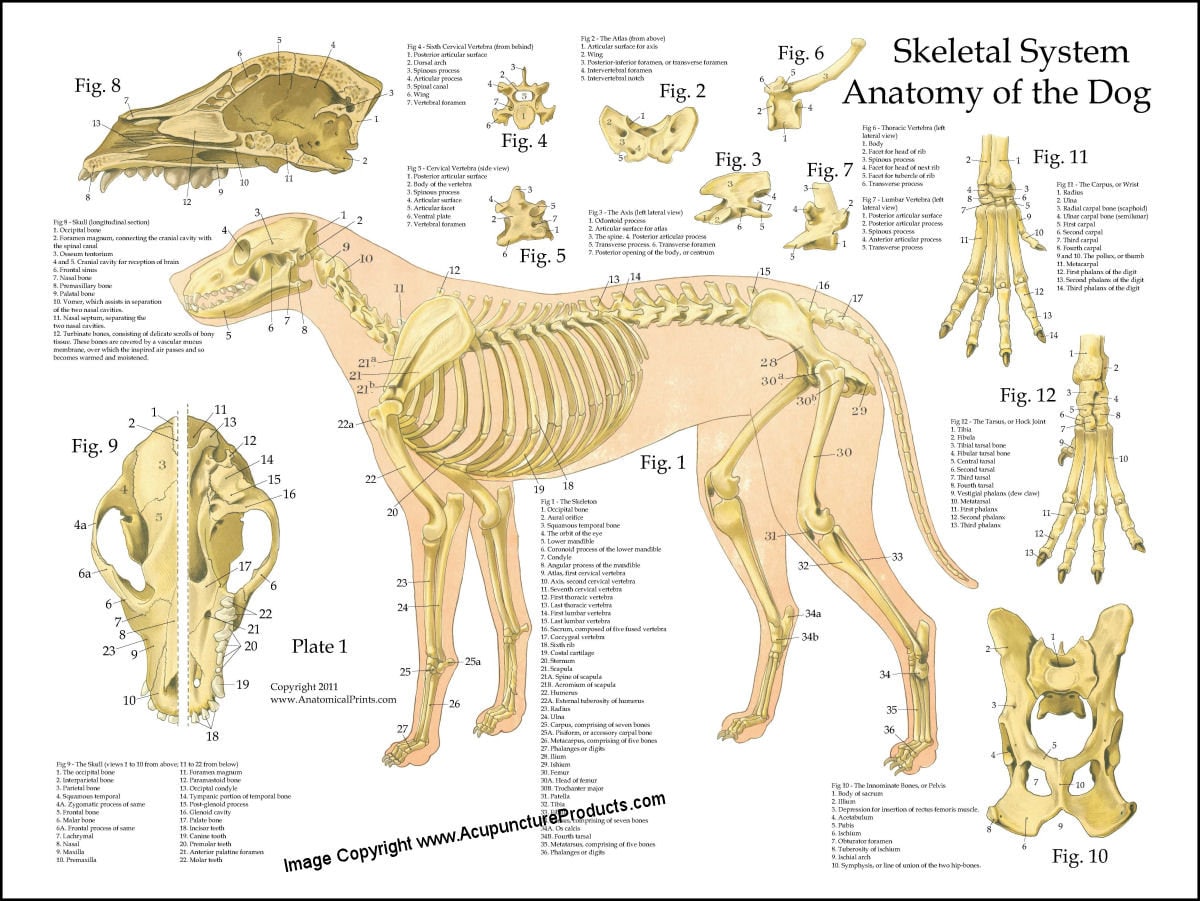
Dog Skeletal Skull Anatomy Poster 18 X 24 Etsy
An overview of the anatomy of the canine skeleton.Follow on twitter @ https://twitter.com/PerkyVetInstagram: Perkydvm
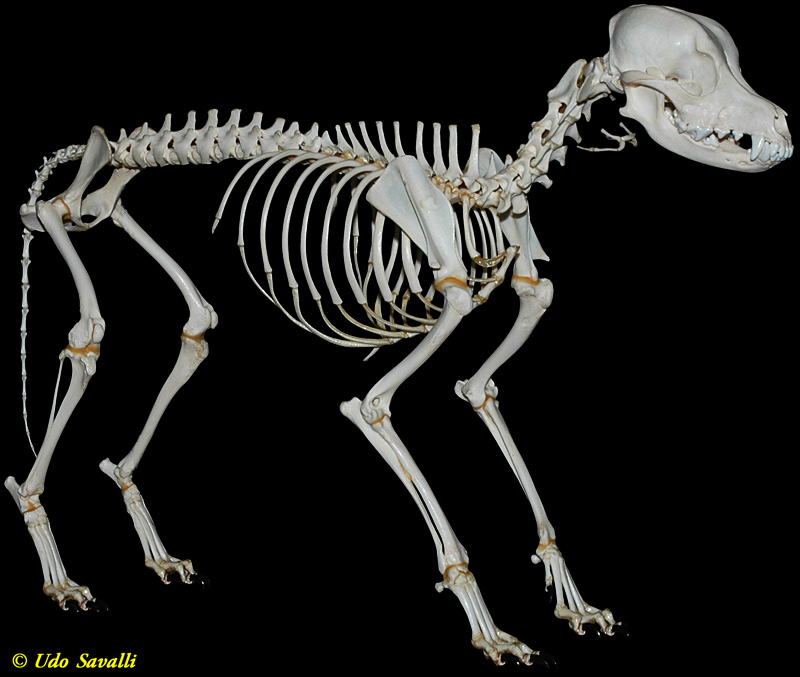
BIO370Mammal Skeletons
January 3, 2024 < http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Dog-Skeletal-Anatomy > Dog Skeletal Anatomy

Dog skeleton 101 Dog Anatomy Bones Animal Hackers
The cat has a small coronoid fossa medial to the radial fossa that accommodates the coronoid process of the ulna during elbow joint flexion.; The cat has a supracondylar foramen near the medial condyle allowing the passage of the median nerve and brachial blood vessels.; There is an intermediate tubercle between the greater and lesser tubercles in the horse's intertubercular groove.

Anatomy of a male dog crosssection, showing the skeleton and internal
Directional Terms and Anatomic Planes Directional Terms from Normal Stance (Anatomic Position) The dog stands upright on digits or phalanges of each forepaw or manus and each hindpaw or pes (Figure 5-1). This type of stance is termed a digitigrade stance.

Dog skeleton with major bone elements labeled (Davis, 1987, p. 54
Components of the Musculoskeletal System in Dogs. Bones provide rigid structure to the body and shield internal organs from damage. They also house bone marrow, where blood cells are formed, and they maintain the body's reservoirs of calcium and phosphorus. Old bone tissue is constantly replaced with new bone tissue in a process called.